Latency Troubleshooting using vRNI
In the blog,
Latency Monitoring using vRNI
we learnt how can we use Aria Operations for Network to Monitor
Latency.
But the next part is how do we determine what is the exact cause for the
Latency.
In this blog, we will determine which portion of the traffic is responsible for increasing latency in the environment.
Let’s run the following query in Aria Operations for Network,
netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond,
netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.average.microsecond,vm1, vm2,
virtualInterface1, virtualInterface2 of interface pair info where host
is set and virtualInterface1Type != VMKNIC and
netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond > 0 order by
netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond limit 10
When we run the above query, it will give us a list of the top 10 vNIC-vNIC pairs with high latency between them.
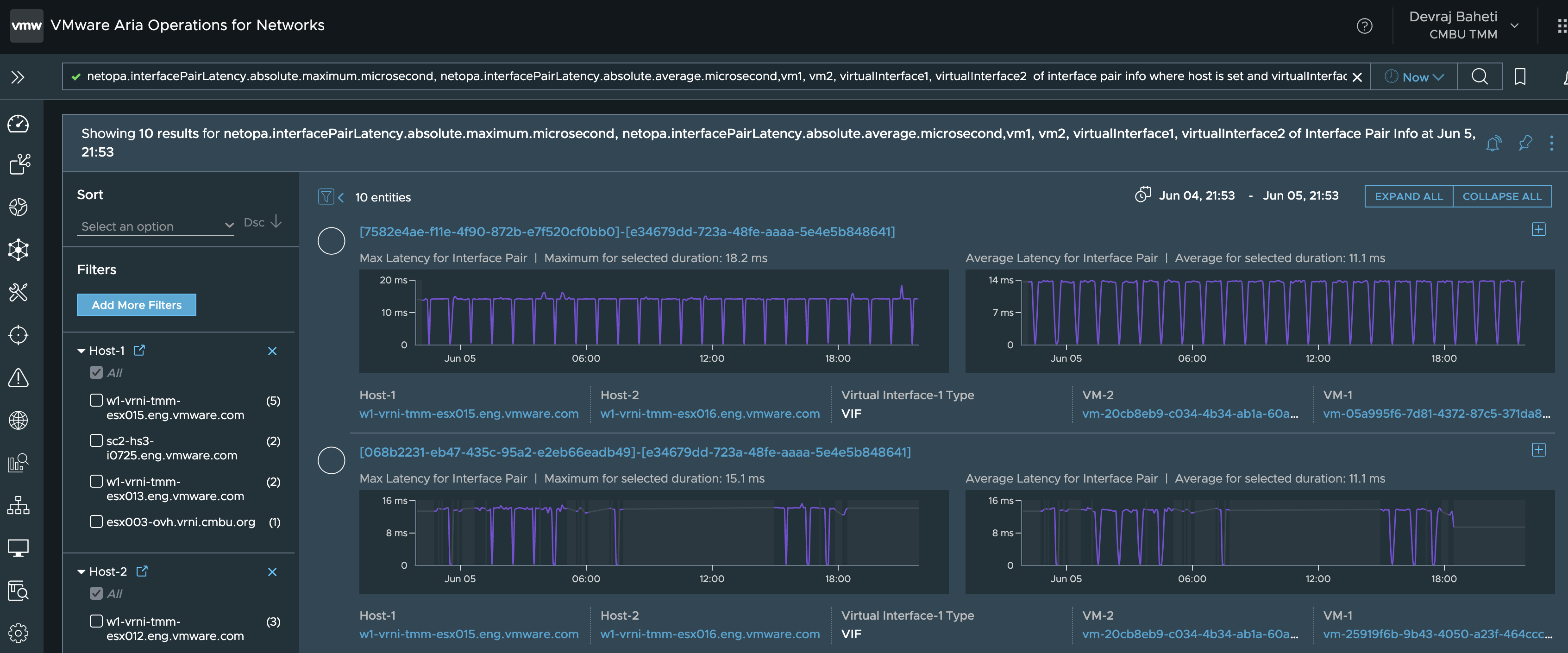
The overall vNIC-vNIC Latency consists of the following components. The details have been captured in the previous blog mentioned above.
- Src VM -> Src PNIC (vNIC - PNIC)
- Src VTEP -> Dst VTEP (VTEP - VTEP)
- Dst PNIC -> Dst VM (PNIC - vNIC)
Now, we need to identify which of the above 3 components is causing high
vNIC-vNIC Latency.
It will help us to pinpoint the component responsible and investigate
further.
To determine the latency between the above-mentioned components, we need to run the following queries.
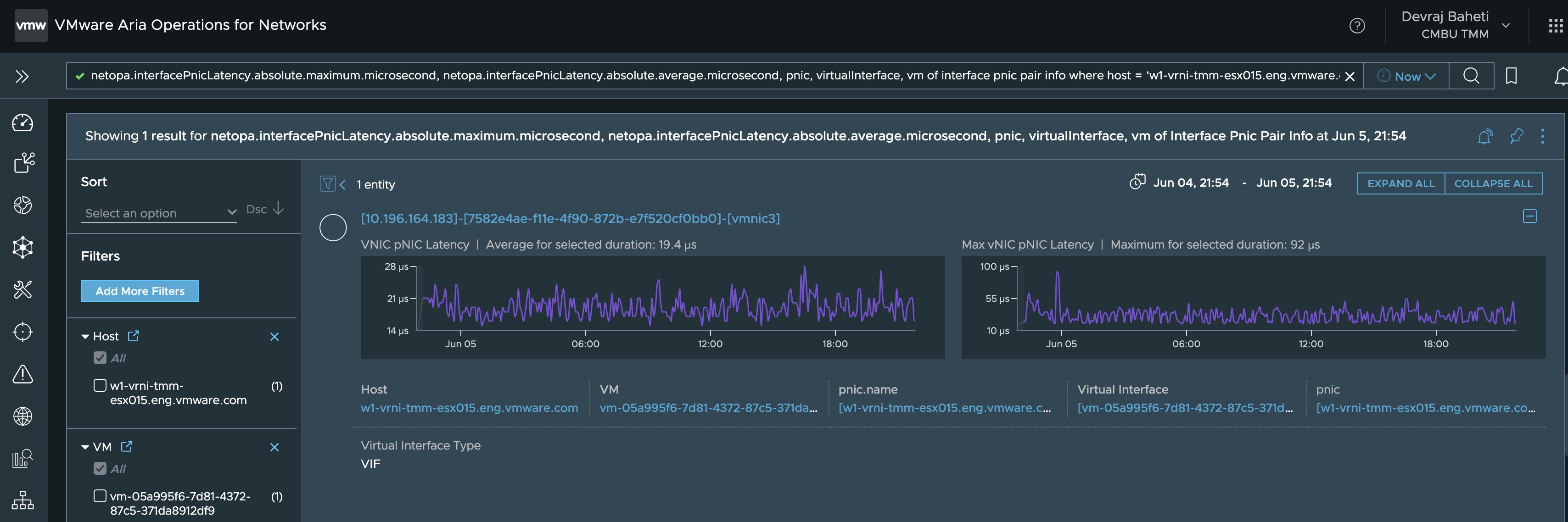
- Src VM -> Src PNIC (vNIC - PNIC)
netopa.interfacePnicLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond, netopa.interfacePnicLatency.absolute.average.microsecond, pnic, virtualInterface, vm of interface pnic pair info where host = 'src-host' and vm = 'src-vm' OR vNIC PNIC Latency, max vNIC PNIC Latency, pnic, virtualInterface, vm of interface pnic pair info where host = 'src-host' and vm = 'src-vm'
In the above query, we replace the src-host and src-vm with the name of the source host and source VM.
This will give us the latency of the first component.
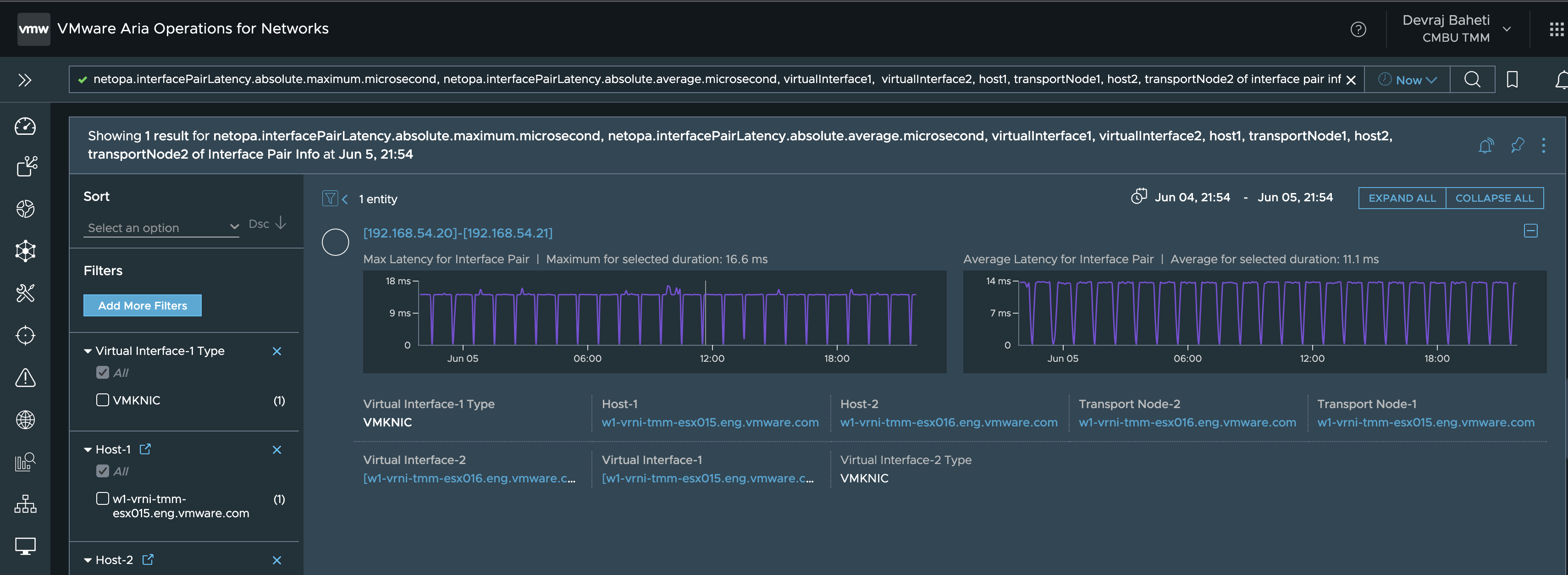
- Src VTEP -> Dst VTEP (VTEP - VTEP)
netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond, netopa.interfacePairLatency.absolute.average.microsecond, virtualInterface1, virtualInterface2, host1, transportNode1, host2, transportNode2 of interface pair info where virtualInterface1Type = VMKNIC and host1 = 'src-host'
In the above query, we replace the src-host and dst-host with the name of the source host and destination host.
The src-host and dst-host names can be obtained from the initial query run to get the vNIC-vNIC Latency.
This will give us the latency of the second component.
- Dst PNIC -> Dst VM (PNIC - vNIC)
netopa.pnicInterfaceLatency.absolute.maximum.microsecond, netopa.pnicInterfaceLatency.absolute.average.microsecond, pnic, virtualInterface, vm of interface pnic pair info where host = 'dst-host' and vm = 'dst-vm' OR PNIC vNIC Latency, max PNIC vNIC Latency,pnic, virtualInterface, vm of interface pnic pair info where host = 'dst-host' and vm = 'dst-vm'
In the above query, we replace the dst-host and dst-vm with the name of the destination host and destination VM.
This will give us the latency of the third component.
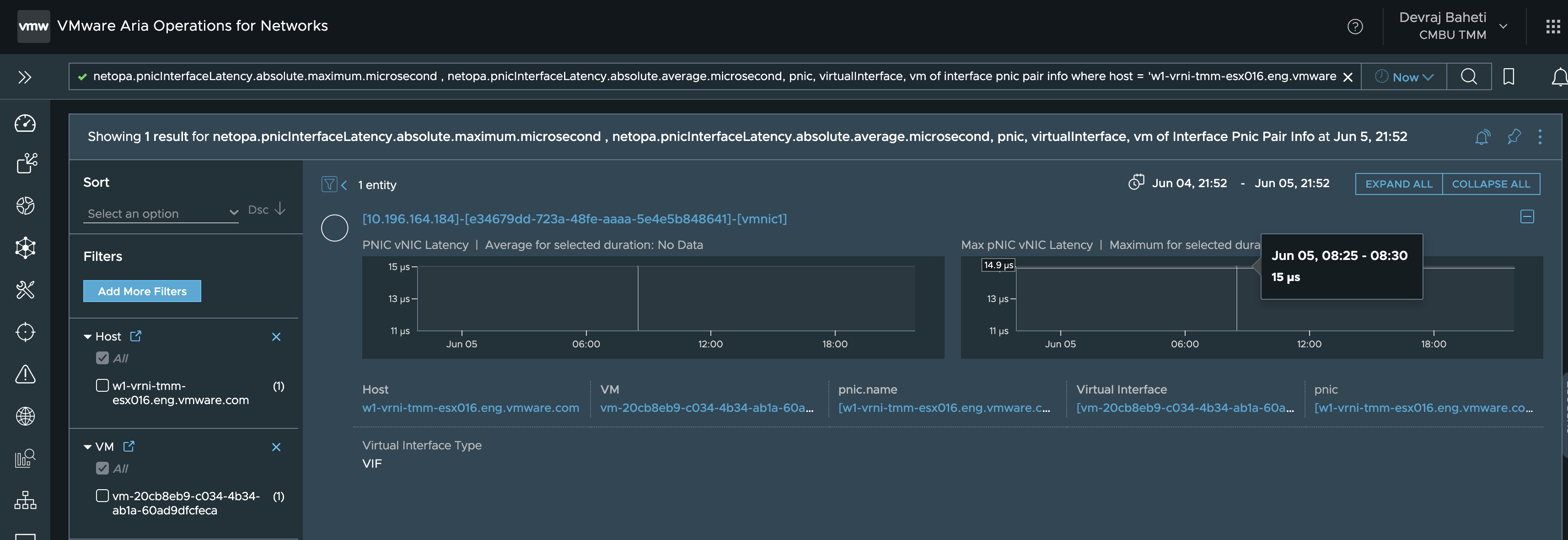
Based on the result of the above queries we will be able to determine
which component is responsible for high vNIC-vNIC latency.
From the above-mentioned screenshots, we can see that the VTEP-VTEP
latency is causing high vNIC-vNIC latency.